What besides digital ad fraud is the largest criminal enterprise currently?
Organized crime encompasses various illegal activities, and identifying a single “largest” criminal enterprise can be challenging due to the diversity and global nature of criminal activities. However, some criminal enterprises are notably significant due to their scale, impact, and global reach:
- Drug Trafficking: Drug cartels and trafficking networks involved in the production, transportation, and distribution of illegal drugs, such as cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, and synthetic opioids, remain a major criminal enterprise globally.
- Human Trafficking: The illegal trade of humans for purposes such as forced labor, sexual exploitation, or organ harvesting is a significant and disturbing criminal enterprise that operates worldwide.
- Cybercrime: With the rise of the internet, cybercrime has become a substantial criminal enterprise involving activities like hacking, identity theft, phishing, ransomware attacks, and financial fraud. Cybercriminal organizations often operate internationally and can cause significant financial losses.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade: Criminal networks involved in the illegal trade of endangered species, exotic animals, and animal parts operate across borders, contributing to the endangerment of species and ecological imbalances.
- Money Laundering: Criminal organizations engage in money laundering to legitimize the proceeds of their illegal activities. This involves disguising the origins of illegal funds by integrating them into the legitimate financial system.
- Arms Trafficking: Illicit arms trafficking networks facilitate the illegal trade of firearms, ammunition, and military-grade weapons, contributing to regional conflicts, violence, and instability.
The scale and impact of these criminal enterprises vary, and addressing them requires international cooperation, law enforcement efforts, legislative measures, and targeted strategies aimed at disrupting these networks and reducing their influence.
Know the reason , Why does ad fraud continue to trouble the digital industry?
Ad fraud persists in the digital advertising industry due to several persistent challenges:
- Sophisticated Techniques: Fraudsters constantly evolve their tactics. As soon as new measures are implemented to counter fraud, they find new ways to bypass these defenses. Their ability to adapt quickly makes it challenging to stay ahead of fraudulent activities.
- Profit Incentive: Ad fraud is lucrative. Fraudsters can generate substantial profits by tricking advertisers through fake impressions, clicks, or conversions. As long as there’s money to be made, there will be individuals or groups motivated to engage in fraudulent activities.
- Complex Ecosystem: The digital advertising ecosystem involves multiple players—advertisers, publishers, ad networks, ad exchanges, etc. Each point in this complex supply chain can be vulnerable to exploitation, making it difficult to pinpoint and address fraudulent activities.
- Lack of Industry Standards and Collaboration: While there are efforts to establish standards and best practices, the industry lacks universal guidelines or regulations to combat ad fraud effectively. Moreover, collaboration among different stakeholders—advertisers, publishers, ad tech companies—is sometimes limited, hindering a unified approach to tackle fraud.
- Growing Digital Landscape: With the expansion of digital platforms, including social media, mobile apps, video streaming, etc., the surface area for potential ad fraud increases. Each new platform or technology presents new opportunities for fraudsters to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Global Nature of the Internet: Ad fraud is not confined by borders. It’s a global issue, and perpetrators can operate from anywhere in the world, making it difficult to enforce regulations or take legal action against them.
- Complexity in Measurement and Detection: The diversity of ad formats, devices, and user behaviors makes it challenging to accurately measure and detect fraudulent activities. The sheer volume of data and the need for real-time analysis add to the complexity.
Addressing ad fraud requires a multifaceted approach that involves technological advancements, industry collaboration, regulatory efforts, and ongoing vigilance. While progress has been made in combating ad fraud, its persistence underscores the need for continued innovation and cooperation within the digital advertising ecosystem.
Know about digital ad fraud, and how is it going to collapse?
Digital ad fraud refers to deceptive or malicious activities that exploit the online advertising ecosystem for illegitimate gains. It encompasses various fraudulent techniques aimed at generating fake ad impressions, clicks, or conversions, leading to financial losses for advertisers and undermining the effectiveness and integrity of digital advertising.
Here are some common types of digital ad fraud:
Bot Traffic: Automated bots mimic human behavior to generate fake impressions, clicks, or engagement on ads. These bots can inflate ad metrics and waste advertisers’ budgets.
Click Fraud: Fraudulent clicks on ads are generated by individuals, scripts, or automated programs, aiming to drive up advertising costs for competitors or exhaust an advertiser’s budget.
Ad Stacking and Pixel Stuffing: Techniques where multiple ads are stacked on top of each other, or ads are placed in small, invisible pixels, leading to multiple ad impressions being served without being seen by users.
Domain Spoofing: Fraudsters misrepresent their websites to appear as legitimate, well-known sites to get higher ad rates or trick advertisers into thinking their ads are being displayed on reputable sites.
Cookie Stuffing: Placing cookies on users’ devices without their consent to earn commissions for fake referral traffic or clicks.
Addressing digital ad fraud is an ongoing challenge in the advertising industry, and various strategies are being implemented to combat it:
Ad Verification Technology: Advanced tools and technologies are used to verify the legitimacy of ad impressions and detect fraudulent activities in real-time.
Fraud Detection Algorithms: Machine learning and AI-based algorithms are employed to analyze patterns and identify fraudulent behavior, helping to flag suspicious activities.
Blockchain and Transparency: Some initiatives use blockchain technology to increase transparency and traceability in the digital advertising supply chain, reducing the risk of fraud by providing a transparent ledger of transactions.
Industry Collaboration and Standards: Collaboration among industry players, adherence to standardized practices, and the implementation of stringent guidelines help create a more secure and trustworthy advertising environment.
While these efforts are helping in mitigating digital ad fraud, fraudsters are continuously evolving their tactics. The fight against ad fraud is ongoing, and it requires a collective effort from advertisers, publishers, ad tech companies, and industry regulators to create a more transparent and secure digital advertising ecosystem. The goal is not necessarily to “collapse” fraud entirely but to significantly reduce its prevalence and impact on the industry.
Know how big of a deal is the digital ad fraud? How much does it affect us?
Digital ad fraud is a significant issue in the advertising industry, impacting advertisers, publishers, and consumers in various ways. Its effects are substantial and wide-ranging:
Financial Losses: Advertisers lose billions of dollars annually due to fraudulent activities. Fraudulent ad impressions, clicks, or conversions waste advertising budgets, reducing the return on investment (ROI) of ad campaigns.
Credibility and Trust: Fraud undermines the credibility and trust within the digital advertising ecosystem. Advertisers lose faith in the effectiveness of online advertising, which can lead to decreased investment in digital channels.
Impact on Publishers: Publishers might unknowingly host fraudulent ads or experience reduced ad revenue due to advertisers pulling back budgets in response to fraud concerns. This affects their sustainability and ability to produce quality content.
User Experience: Fraudulent ads often lead to poor user experiences. Users may encounter misleading or irrelevant ads, impacting their trust in online advertising and potentially harming brand reputation.
Adoption of Ad-Blocking Software: Concerns about fraudulent and intrusive ads have contributed to the rise in ad-blocking software adoption. This further challenges the effectiveness of online advertising as ads are blocked, reducing their reach.
Economic Impact: The economic impact of digital ad fraud goes beyond advertising budgets. It affects the broader economy as businesses might cut back on spending, impacting job creation and innovation within the advertising and digital industries.
The exact magnitude of digital ad fraud is challenging to quantify precisely due to its complex and evolving nature. Estimates vary, but several studies suggest that billions of dollars are lost annually to ad fraud globally.
Efforts to combat fraud, including advancements in technology, industry collaboration, and increased awareness, aim to reduce its impact. However, fraudsters continuously adapt their tactics, making it an ongoing challenge for the advertising ecosystem.
While digital ad fraud poses significant challenges, ongoing initiatives and evolving strategies are working toward mitigating its effects, aiming for a more transparent, trustworthy, and secure digital advertising environment.
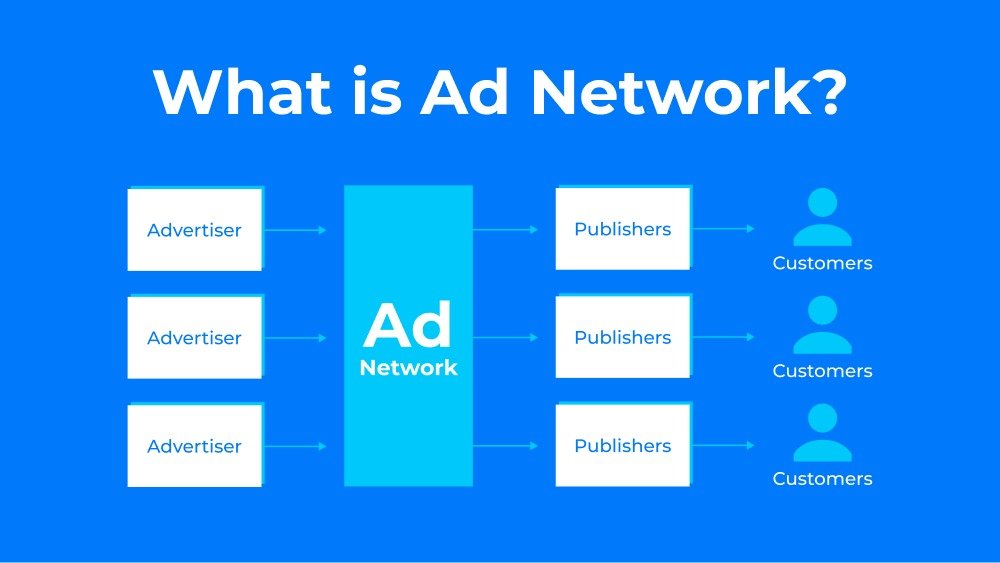
Know about ad network and how does it work
An ad network is a platform that connects advertisers with publishers to facilitate the buying and selling of online advertising space. It serves as an intermediary between advertisers who want to promote their products or services and publishers who have available space on their websites, apps, or other digital platforms to display ads.
Here’s a breakdown of how an ad network typically operates:
Aggregation of Ad Inventory: Ad networks gather ad space from various publishers into a centralized platform, creating a pool of advertising inventory. This inventory includes different types of ad formats like banners, videos, native ads, etc.
Ad Targeting and Campaign Setup: Advertisers specify their target audience and campaign objectives. They set criteria such as demographics, interests, geography, and behavior to reach the most relevant users. Ad networks help match these criteria with available ad space that fits the advertiser’s target audience.
Auction or Fixed Price Models: Ad space can be sold through auctions (real-time bidding) where advertisers bid for ad placements, or through fixed-price models where the cost is predetermined.
Ad Placement and Delivery: Once an ad is selected based on the targeting criteria, the ad network places the ad on the publisher’s website or app. The network manages the delivery of ads to the intended audience.
Performance Tracking and Analytics: Ad networks provide analytics and reporting tools for both advertisers and publishers. They track the performance of ads in terms of impressions, clicks, conversions, and other relevant metrics. This data helps optimize campaigns for better results.
Revenue Sharing: Ad networks handle the financial aspects, collecting payments from advertisers and distributing revenue to publishers based on ad performance and agreed-upon terms.
Ad networks vary in size, specialization, and technology. Some focus on specific industries or ad formats, while others cover a wide range of audiences and formats. Additionally, with advancements in technology, programmatic advertising has become prevalent within ad networks, allowing for automated buying and selling of ads based on algorithms and real-time data.
Overall, ad networks play a critical role in online advertising, helping advertisers effectively reach their target audience while enabling publishers to monetize their digital properties by selling ad space.
what is ad exchange in adnetwork
An ad exchange is a digital marketplace where advertisers and publishers come together to buy and sell advertising space programmatically. It serves as a platform for the automated buying and selling of online advertising inventory.
Here’s how an ad exchange typically operates within an ad network ecosystem:
Real-Time Bidding (RTB): Ad exchanges often utilize real-time bidding, an auction-based system where ad impressions are sold and bought in real-time. When a user visits a website or app, information about that impression (user data, context of the visit, etc.) is sent to the ad exchange.
Auction Process: Advertisers or their representatives (such as demand-side platforms or DSPs) bid on these impressions based on criteria like user demographics, browsing behavior, and other targeting parameters. The highest bidder wins the opportunity to display their ad to that user.
Programmatic Buying and Selling: Ad exchanges enable programmatic buying, which allows advertisers to target specific audiences and bid for ad impressions across multiple websites or apps simultaneously. Similarly, publishers can sell their ad inventory to multiple advertisers without negotiating directly.
Transparency and Control: Ad exchanges provide transparency in the buying and selling process. Advertisers and publishers have control over the types of ads they want to display or sell, the pricing, and the targeting criteria.
Efficiency: By automating the buying and selling of ad inventory, ad exchanges streamline the process, making it more efficient and cost-effective for both advertisers and publishers.
Data Utilization: Ad exchanges often leverage data management platforms (DMPs) to enhance targeting capabilities. They use data analysis to improve ad targeting and performance, providing more relevant ads to users.
Ad exchanges play a crucial role in the programmatic advertising landscape by facilitating the automated buying and selling of ad inventory in real-time. They enable advertisers to reach their target audiences more precisely and allow publishers to monetize their digital properties more effectively by maximizing the value of their ad space.
What is an ad server in adnetwork
An ad server is a core component of an ad network, serving as the technological infrastructure that manages the delivery of online advertisements to users’ devices. It acts as a central hub that stores, delivers, and tracks digital ads across websites, apps, or other digital platforms.
Here’s how an ad server typically functions within an ad network:
Ad Storage: Ad servers store various ad creatives (such as banners, videos, interactive ads) uploaded by advertisers or agencies. These creatives are tagged with information specifying the targeting criteria and instructions for their display.
Targeting and Delivery: Ad servers use targeting parameters (like user location, browsing behavior, device type) to determine which ad to display to a specific user. When a user visits a website or app that is part of the ad network, the ad server selects the most relevant ad from its inventory to display.
Rotation and Frequency Capping: Ad servers often manage ad rotation to prevent users from seeing the same ad repeatedly. They also implement frequency capping to control the number of times a particular ad is shown to a user within a specific time frame.
Tracking and Reporting: Ad servers track the performance of ads by recording metrics such as impressions, clicks, conversions, and other engagement-related data. This information is used to generate reports for advertisers and publishers, offering insights into the effectiveness of their campaigns or ad placements.
Ad Trafficking: Ad servers handle the process of ad trafficking, which involves setting up and scheduling ad campaigns, specifying targeting criteria, and managing the delivery of ads across different websites or apps within the ad network.
Optimization: Advanced ad servers often include optimization algorithms that adjust ad delivery based on real-time performance data, aiming to improve campaign effectiveness and maximize returns for advertisers and publishers.
Ad servers are crucial in managing the complexity of ad networks by efficiently delivering targeted ads to the right users at the right time, while also providing valuable insights and control to advertisers and publishers.
Know about ad network in marketing
Sure, ad networks are platforms that connect advertisers with publishers to facilitate the buying and selling of online advertising space. They act as intermediaries, bringing together advertisers who want to promote their products or services and publishers who have ad space on their websites or apps.
Here’s how they generally work:
Aggregation: Ad networks aggregate ad space from various publishers into one platform, creating a pool of advertising inventory.
Matching: Advertisers can target specific audiences or demographics based on factors like location, interests, browsing history, etc. The ad network matches these criteria with available ad space that fits the advertiser’s target audience.
Auction or Fixed Price: Ad space can be sold through auctions (where advertisers bid for ad placements in real-time) or through fixed-price models.
Delivery: Once an ad is placed, the network manages the delivery of the ad to the appropriate audience across the publisher’s websites or apps.
Analytics and Reporting: Ad networks often provide analytics and reporting tools for both advertisers and publishers, allowing them to track the performance of their ads or ad spaces in terms of clicks, impressions, conversions, etc.
There are different types of ad networks:
Vertical Ad Networks: Focused on specific industries or niches, like technology, fashion, or finance.
Horizontal Ad Networks: Cover a wide range of industries and audiences.
Mobile Ad Networks: Specifically geared towards mobile app advertising.
Video Ad Networks: Specialize in video-based ad placements.
Ad networks play a crucial role in online advertising, helping advertisers reach their target audience more effectively and enabling publishers to monetize their online traffic. However, with the growth of programmatic advertising and other technologies, some traditional ad networks have evolved or faced challenges in adapting to newer advertising methods and platforms.
Programmatic Advertising: Revolutionizing Ad Networks in the Digital Age
In today’s digital age, traditional advertising methods are gradually giving way to more efficient and data-driven strategies. Programmatic Advertising stands at the forefront of this evolution, allowing advertisers to precisely target their audience and publishers to maximize their ad revenue. Let’s embark on a journey to understand how Programmatic Advertising is revolutionizing ad networks and what it means for the digital advertising landscape.
Traditional Advertising vs. Digital Advertising
In the ever-evolving landscape of advertising, the shift from traditional to digital methods has been nothing short of revolutionary. Traditional advertising, comprising print, TV, and radio, has long been the bedrock of marketing campaigns. However, the rise of digital advertising has completely transformed the way businesses reach and engage their audiences.
Digital advertising offers unparalleled precision and targeting. Through data analytics and user behavior tracking, advertisers can tailor their messages to specific demographics, ensuring that their content reaches the right people at the right time. This level of personalization was nearly impossible with traditional methods.
Moreover, digital advertising is highly cost-effective. Unlike the substantial costs associated with producing and airing television or radio commercials, digital ads can be created and launched with relative ease, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes. This democratization of advertising has expanded opportunities for startups and small businesses.
Traditional advertising still holds value, especially in building brand recognition, but it lacks the interactive and data-driven capabilities that make digital advertising so effective in the modern age. The shift towards digital advertising is a reflection of the changing consumer landscape, where people spend an increasing amount of time online, and businesses must adapt to remain relevant.
Emergence of Ad Networks
One significant development in the digital advertising realm is the emergence of ad networks. These networks act as intermediaries, connecting advertisers with a vast array of websites and online platforms where their ads can be displayed. This creates a more streamlined and efficient approach to digital advertising.
Ad networks offer advertisers access to a diverse range of websites, apps, and social media platforms, allowing them to reach a broad audience. These networks often use real-time bidding and advanced algorithms to optimize ad placement, ensuring that ads are displayed to users who are more likely to engage with the content.
Limitations of Traditional Ad Networks
Traditional ad networks, which existed primarily in the early days of digital advertising, had their limitations. They often struggled with ad fraud and click fraud, where false clicks and impressions inflated costs without delivering genuine engagement. Additionally, they faced challenges in targeting and personalization compared to more advanced digital ad networks.
The evolution of digital advertising and ad networks has addressed many of these limitations. Sophisticated algorithms and machine learning capabilities now allow for precise targeting and real-time optimization, minimizing wasted ad spend and improving the overall effectiveness of campaigns.
What is Programmatic Advertising?
Programmatic advertising is a sophisticated, data-driven approach to digital marketing that has revolutionized the way online ads are bought and placed. Unlike traditional advertising methods, which involve manual negotiations and ad placement, programmatic advertising uses automated systems and algorithms to purchase and display ads. This process streamlines the ad-buying process and optimizes campaign performance.
Programmatic advertising leverages technology and real-time data to target specific audiences across various digital channels, such as websites, mobile apps, and social media. It allows advertisers to reach their intended audience with precision, ensuring that the right message is delivered to the right person at the right time.
How Programmatic Advertising Works
Programmatic advertising operates through a complex yet efficient ecosystem. Advertisers, through demand-side platforms (DSPs), input their campaign parameters, budget, and target audience. Publishers, on the other hand, make their ad inventory available through supply-side platforms (SSPs). These platforms connect the two sides and facilitate the entire process.
One of the key mechanisms at the heart of programmatic advertising is Real-time Bidding (RTB). When a user visits a webpage, the ad space is put up for auction in real-time. Advertisers bid on this space based on user data and the context of the page. The highest bidder wins and their ad is displayed to the user. This entire process takes milliseconds, ensuring that the right ad is shown to the right user at the right moment.
Ad Networks in the Digital Age
Key Components of Programmatic Advertising
Real-time Bidding (RTB):
RTB is the backbone of programmatic advertising. It enables advertisers to compete in auctions to display their ads in real-time, making the process incredibly efficient. Advertisers bid based on user data and contextual factors, ensuring the ad’s relevance to the user.
Data-driven Targeting:
Programmatic advertising relies on data to target the right audience. Advertisers can use a wealth of data, including demographics, behavior, and location, to pinpoint their ideal customers. This precise targeting increases the chances of engagement and conversions.
Automation and Efficiency:
Automation is a fundamental aspect of programmatic advertising. It reduces the need for manual intervention, which not only saves time but also optimizes ad placements. Automated algorithms make split-second decisions, ensuring that each impression counts.
Improved Targeting and Personalization
Programmatic advertising revolutionizes how brands connect with their audience by providing unparalleled targeting capabilities. Through advanced algorithms and access to vast data sources, advertisers can pinpoint their ideal customers with precision. This level of targeting ensures that your ads reach the right people at the right time, ultimately increasing the chances of conversions.
Moreover, programmatic advertising enables personalization at scale. Advertisers can tailor ad creatives and messaging to match the preferences and behaviors of individual users. This personal touch enhances user engagement and boosts the overall effectiveness of your campaigns.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
One of the most appealing aspects of programmatic advertising is its cost-effectiveness. It optimizes your ad spend by allocating budget to the most promising opportunities in real-time. With automated bidding strategies, you can reduce wasted ad spend on uninterested audiences and focus on those who are likely to convert. This level of efficiency means that every dollar you invest has the potential to generate higher returns.
Real-Time Optimization
Programmatic advertising operates in real-time, allowing for on-the-fly adjustments to campaigns. Advertisers can fine-tune their strategies based on real-time data, such as click-through rates and conversion rates. This adaptability ensures that your ads are always performing at their peak and that you’re not locked into static, unproductive campaigns.
Enhanced Reporting and Analytics
Data-driven decision-making is a hallmark of programmatic advertising. The technology offers comprehensive reporting and analytics tools that provide deep insights into campaign performance. Advertisers can track metrics like impressions, click-through rates, and conversions, enabling them to make data-driven adjustments for better results. These insights help refine future campaigns and maximize the ROI.
Ad Fraud and Viewability Issues
Ad fraud and viewability issues are persistent challenges in programmatic advertising. Ad fraud occurs when fraudulent websites and bots mimic legitimate traffic, generating fake ad impressions and clicks. This not only wastes advertising budgets but also tarnishes the credibility of programmatic advertising. Viewability concerns, on the other hand, revolve around ensuring that ads are actually seen by real users. In some cases, ads may load below the fold or be obstructed by other content, resulting in lower viewability rates.
To combat ad fraud and viewability issues, advertisers must invest in fraud detection and prevention tools. Utilizing sophisticated algorithms, machine learning, and AI, these tools can identify irregularities in traffic patterns and help block fraudulent impressions. Advertisers should also work with reputable publishers and demand transparency in their programmatic supply chain to maximize viewability.
Privacy and Data Protection Concerns
Privacy and data protection concerns have gained prominence in the programmatic advertising landscape, particularly with the introduction of regulations like GDPR and CCPA. These regulations require advertisers to obtain explicit consent from users to collect and use their data for targeting purposes. This has led to a more stringent approach to data handling and ad targeting.
To address privacy concerns, advertisers must implement robust consent mechanisms, ensure transparent data handling practices, and work with Data Management Platforms (DMPs) that provide strong data protection features. It’s crucial to stay informed about evolving privacy regulations and adapt strategies accordingly to avoid legal and reputational risks.
Ad Blocking and Brand Safety
Ad blocking, often driven by user frustration with intrusive or irrelevant ads, poses a significant challenge to programmatic advertising. It restricts the reach and effectiveness of ad campaigns. Additionally, ensuring brand safety is crucial, as ads may inadvertently appear alongside objectionable or harmful content, damaging a brand’s reputation.
To combat ad blocking, advertisers should focus on delivering non-intrusive, relevant, and engaging ads that add value to the user experience. They can also use tools to detect ad-blocker usage and adjust their approach accordingly. For brand safety, leveraging content verification tools and working with trusted publishers and exchanges is essential. Employing keyword targeting and contextual analysis can also help ensure ads appear in safe and relevant environments.
AI’s Impact on Ad Targeting and Optimization
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the landscape of programmatic advertising, especially in the realm of ad targeting and optimization. It has become an indispensable tool for advertisers and marketers, offering precise and data-driven methods to reach the right audience with the right message at the right time.
AI enables highly granular ad targeting by analyzing vast datasets and user behavior. Through machine learning algorithms, it can identify patterns and preferences, making it possible to create audience segments based on various criteria such as demographics, interests, and browsing history. This level of precision ensures that ad spend is maximized by reaching only the most relevant potential customers.
One of the remarkable features of AI is its real-time decision-making capabilities. It can adjust bids and ad placements dynamically, based on the performance of ads in real-time. This adaptive approach minimizes wasted ad spend on underperforming placements and maximizes returns on the best-performing ones.
Additionally, AI can optimize ad creatives to improve engagement and conversion rates. It can conduct A/B testing at scale and identify the most effective ad copy and visuals. This continuous optimization enhances the overall quality of advertisements and ensures that the creative resonates with the target audience.
Use of Machine Learning in Programmatic Advertising
Machine learning is a fundamental component of AI, and its role in programmatic advertising is pivotal. It empowers advertisers to make data-driven decisions, automate processes, and predict future trends.
One of the primary applications of machine learning is predictive analytics. Advertisers can use historical data to predict user behavior, ad performance, and market trends. This forecasting capability allows for proactive adjustments to advertising strategies, ensuring optimal results.
Machine learning algorithms are also used for bid optimization. They consider various factors, including ad placement, user behavior, and competitive bids, to determine the optimal bid amount for each ad auction. This automation reduces the risk of overpaying for impressions and maximizes the value of every advertising dollar.
Furthermore, machine learning is instrumental in fraud detection. Ad fraud is a significant concern in programmatic advertising, but machine learning algorithms can identify unusual patterns that may indicate fraudulent activities, preventing ad dollars from going to waste.
FAQs
Q: What is Programmatic Advertising?
Programmatic Advertising is an automated method of buying and selling ad space that uses data, algorithms, and real-time auctions to target specific audiences effectively.
Q: How does Programmatic Advertising benefit advertisers?
Programmatic Advertising benefits advertisers by offering enhanced targeting capabilities, real-time optimization, and cost efficiency, resulting in improved ROI.
Q: How has Programmatic Advertising impacted publishers?
Publishers benefit from Programmatic Advertising through increased revenue opportunities and streamlined ad operations, reducing manual intervention.
Q: What role does data play in Programmatic Advertising?
Data is fundamental in Programmatic Advertising, allowing for precise audience targeting and real-time optimization of ad campaigns.
Q: Is Programmatic Advertising suitable for small businesses?
Yes, Programmatic Advertising can be tailored to suit the needs and budget of small businesses, making it an accessible advertising option.
Q: How can advertisers ensure transparency in Programmatic Advertising?
Transparency in Programmatic Advertising is ensured through data insights, allowing advertisers to see where their ads are displayed and how they perform.
Conclusion
Programmatic Advertising is a game-changer in the digital advertising landscape. It has transformed how advertisers target their audience and how publishers manage ad space, making the entire ecosystem more efficient and transparent. As we move forward in the digital age, Programmatic Advertising will likely continue to evolve, providing even more opportunities for both advertisers and publishers.
The Impact of Ad Blockers on Ad Networks: Challenges and Solutions
Ad networks have long been a fundamental part of the digital advertising landscape, connecting advertisers with publishers and facilitating the display of ads on websites and mobile apps. However, the rise of ad blockers has presented both ad networks and advertisers with a significant challenge. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the impact of ad blockers on ad networks, explore the challenges they bring, and provide effective solutions to overcome these obstacles.